A week ago I was thinking of writing a small Kotlin command line tool to read some local json files. I opened IntelliJ and started a kotlin project with gradle. Everything worked just fine. I could compile and run the output jar file until I imported autovalue. Autovalue uses annotation processor to generate model objects, but IntelliJ just would not invoke annotation processing properly so the compilation failed. I did some research and finally made it to work, and I think these tricks are worth to share.
A side note:
Not long ago I wrote a post about why I am still using autovalue in Kotlin projects Why converting Autovalue class to Kotlin data class may not be “pragmatic” for JSON models at this moment.
Jetbrains is really good at listening to the community. They released two exeprimental features to address the two issues I mentioned in the post:
- Android Parcelable available in version 1.1.4
- Serialization available in version 1.1.50, and it support various formats, including JSON.
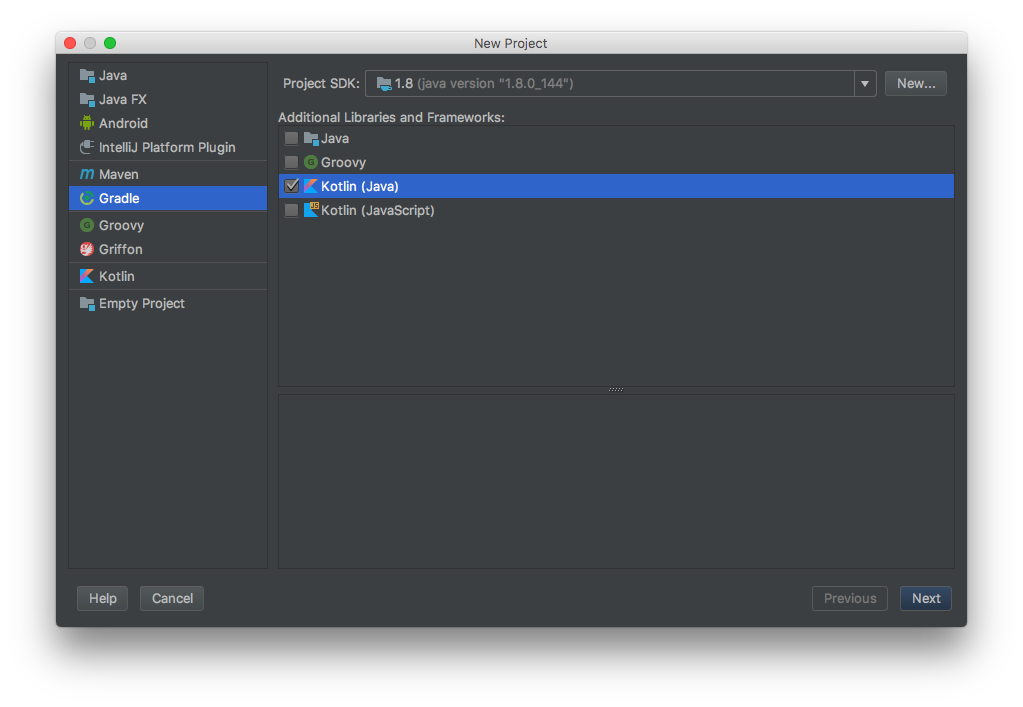
Start a new Kotlin project
Let’s start a new project with Kotlin and gradle supports:
Import the library that uses annotation processing, and enable Kotlin kapt plugin. I use auto value as the example:
| |
jar task reference: Kotlin Basics: Create Executable Kotlin JARs, using Gradle
Lastly we need a simple main method and a autovalue class:
| |
Of course like my comment above, the line val p: Person = AutoValue_Person("Eric", "Lin") just won’t work! But if you run the jar task via gradle in command line directly, you can get a working jar file:
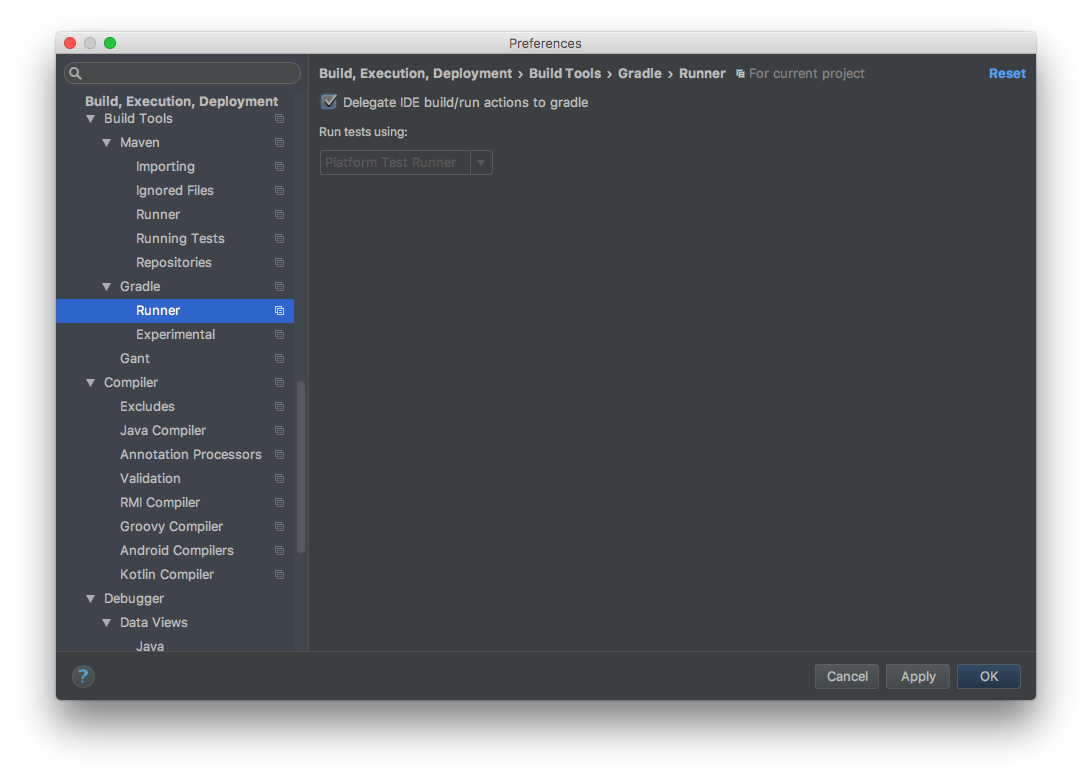
Delegate IDE build/run actions to gradle
The problem here is when you “build” the project, IntelliJ does NOT use the same settings you configure in build.gradle. You must to configure the annotation processor manually, which can be awkward to setup and I could not get it to work properly.
Instead there’s a much simpler trick you can do: Just tell IntellJ to use gradle for your build process!
In Build Tools -> Gradle -> Runner, you can tick the setting Delegate IDE build/run actions to gradle so that IntelliJ will use gradle for your project.
Expose generated files to IntelliJ
Now you can verify the build/generated directory contains the generated files:
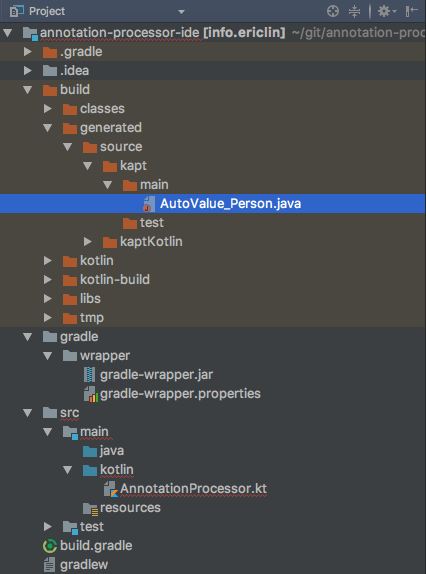
However the file we need AutoValue_Person.java is still not recognized as the source file by the IDE.
There are two ways to mark the kapt directory as source directory:
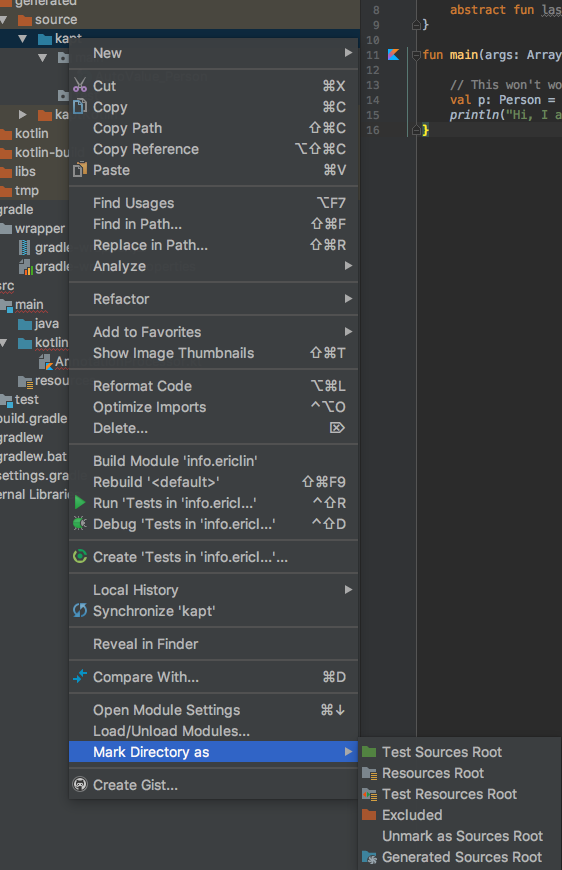
1. Manually mark the directory
Right click on the kapt directory -> Mark Directory as -> Sources Root
2. Use IDEA gradle plugin to mark sources
Add the following snippet to your build.gradle
| |
By doing so the IDEA plugin will configure IntelliJ to treat those two directories as normal source directories.
reference: JetBrains/kotlin-examples
Run and Debug the jar file inside IntelliJ
Now you should be able to compile the project in IntelliJ without any compilation errors. However wouldn’t it be nice if we can run and debug the output jar file in the IDE as well?
Here’s the trick I use:
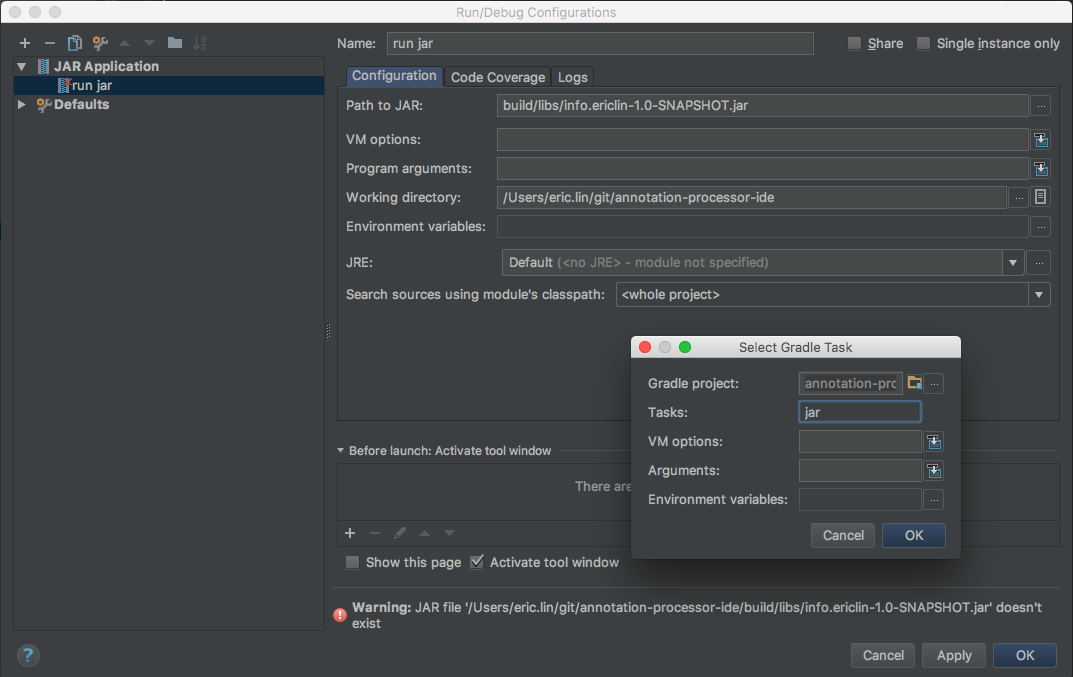
- go to run configuration
- create a Jar Application
- type in the path to the expected output jar file
- in Before Launch settings, add a gradle task
jar
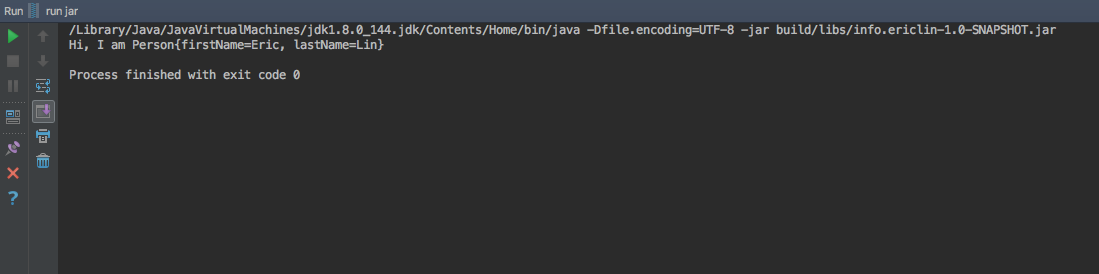
Once the run configuration is set, you should be able to click on run or debug for your compiled jar file inside the IDE!
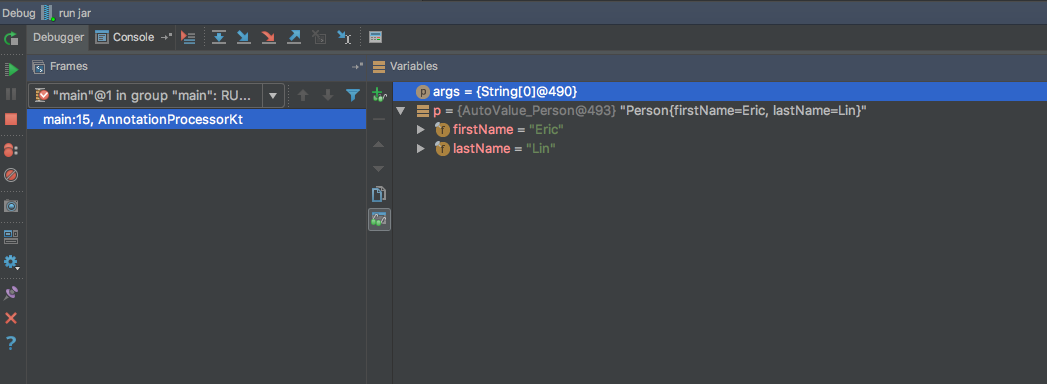
Whoa! Long live Kotlin!